Prostatitis is an inflammatory disease of the prostate gland. It manifests itself from frequent campaigns in the toilet, pain in the penis, scrotum, rectum, sexual disorders (erection, premature ejaculation, etc. ), sometimes delayed urine and blood insurance in the urine. The diagnosis of prostatitis is established by a urologist or other specialist in a typical clinical picture, the results of a rectal study. In addition, an ultrasound of the prostate are performed, sowing the bacteria of prostate secretion and urine. Conservative treatment - Antibacterial therapy, immunotherapy, prostate massage, lifestyle correction.
General information
Prostatitis - inflammation of the seed gland (prostate) - prostate. It is the most common disease of the parental parent system in men. Very often it affects patients aged 25 and 50. In accordance with various data, prostatitis suffers from 30-85% of men over the age of 30. Perhaps abscess the prostate gland, inflammation of the testicles and appendices, which threaten infertility. The ascent of the infection leads to the inflammation of the upper parts of the parental parent system (cystitis, pyelonefrite).
The pathology develops when an infectious agent is inserted, which enters the tissue of the prostate from the organs of the parental parent system (urethra, bladder) or by remote inflammatory focus (with pneumonia, flu, tonsillitis, furunculosis).
The causes of prostatitis
A golden staphylococcus (Enterococcus), Enterobacter (Enterobacter), Pseudomonas (Pseudomonas), Proteus (Proteus) and Klebcelllah and Klebcelllah can act as an infectious agent in an acute process. (Klebsiella) and E. Coli (E. coli). Most microorganisms belong to the conditioned pathogenic flora and cause prostatitis only if there are other predisposing factors. Chronic inflammation is generally caused by Paolo with microbial associations.
The risk of developing the disease increases during hypothermia, the presence of infections and specific conditions in the history of congestion in prostate tissues. The following predisposing factors are distinguished:
- General hypothermia (single or permanent, related to working conditions).
- A sedentary lifestyle, a specialty that forces a person to be in a sitting position for a long time (computer operator, drivers, etc. ).
- Constant constant.
- Violations of the normal rhythm of sexual activity (excessive sexual activity, prolonged abstinence, incomplete ejaculation during the private individual of the emotional coloring of the "usual" sexual relationship).
- The presence of chronic diseases (cholecystitis, bronchitis) or chronic infectious outbreaks in the body (chronic osteomyelitis, absurd caries, tonsillitis, etc. ).
- Urological diseases transferred (urethritis, cystitis, etc. ) and sexual transmission diseases (tricomoniasis, gonorrhea).
- States that cause the inhibition of the immune system (chronic stress, irregular and lower nutrition, regular lack of sleep, a state of surcharge in the athletes).
It is assumed that the risk of developing pathology increases with chronic intoxications (alcohol, nicotine, morphine). Some studies in the field of modern andrology show that the provocative factor is a chronic injury of the horse (vibration, brain emotion) in motorists, motorcyclists and cyclists. However, the overwhelming number of experts believes that all the circumstances listed are not real causes of the disease, but contribute only to the exacerbation of the latent inflammatory process in prostate tissues.
The decisive role in the occurrence of prostatitis is played by stagnation in prostate tissues. The violation of the capillary blood flow causes an increase in lipid peroxidation, edema, the acquittal of the tissues of the prostate and the conditions of the forms for the development of the infectious process.

Symptoms of prostatitis
Acute prostatitis
There are three phases of acute prostatitis, which are characterized by the presence of a certain clinical picture and morphological changes:
- Acute phlegm. Patients complain of rapid, often painful urination, pain in the sacred and perineum.
- Acute follicular. The pain becomes more intense, sometimes they irradiate towards the anus, intensifies during defecation. Stilling is difficult, urine flows with a thin flow. In some cases, the urine delay is noted. Sottocilitis or moderate hyperthermia is typical.
- Acute parenchymal. Pronounced general intoxication, hyperthermia up to 38-40 ° C, chills. Dizuric disorders, often an acute delay in urination. Acute pain and buttons in the perineum. Difficulty defecate.
Chronic prostatitis
In rare cases, chronic prostatitis becomes the result of an acute process, however, normally, a primary chronic path is observed. The temperature occasionally rises to small values. The patient detects a weak pain in the perineum, discomfort during the act of urination and defecation. The most characteristic symptom is the scarce discharge from the urethra during the defecation act. The primary chronic form of the disease develops for a significant period of time. It is preceded by the stagnation of the blood in the capillaries, gradually transforming itself into abotteric prostatitis.
Chronic prostatitis is often a complication of the inflammatory process caused by the causal agent of a specific infection (clamidia, ureaplasma, gonococcus). The symptoms of a specific inflammatory process in many cases mask the manifestations of the prostate injury. A slight increase in pain during urination is possible, weak pain in the perineum, poor discharge from the urethra during defecation. A slight change in the clinical picture often goes unnoticed by the patient.
Chronic inflammation of the prostate gland can be manifested by a burning sensation in the urethra and perineum, dysuria, sexual disorders, increase in general fatigue. The consequence of the violations of the power (or of the fear of these violations) often becomes mental depression, anxiety and irritability. The clinical image does not always include all groups of symptoms listed, differs in different patients and changes over time. There are three main syndrome characteristics of chronic prostatitis: pain, violations when you go to the bathroom, sexual disorders.
There are no pain receptors in prostate tissue. The cause of the pain in chronic prostatitis becomes almost inevitable due to the abundant innervation of the involvement of the pelvic organs in the inflammatory process of the nerve paths. Patients complain of pain of various intensity - from a weak sleep, painful to intense and violated. There is a change in the nature of pain (improvement or weakening) with ejaculation, excessive sexual activity or sexual abstinence. The pain radiates for a scrotum, sacred, horse, sometimes in the lumbar region.
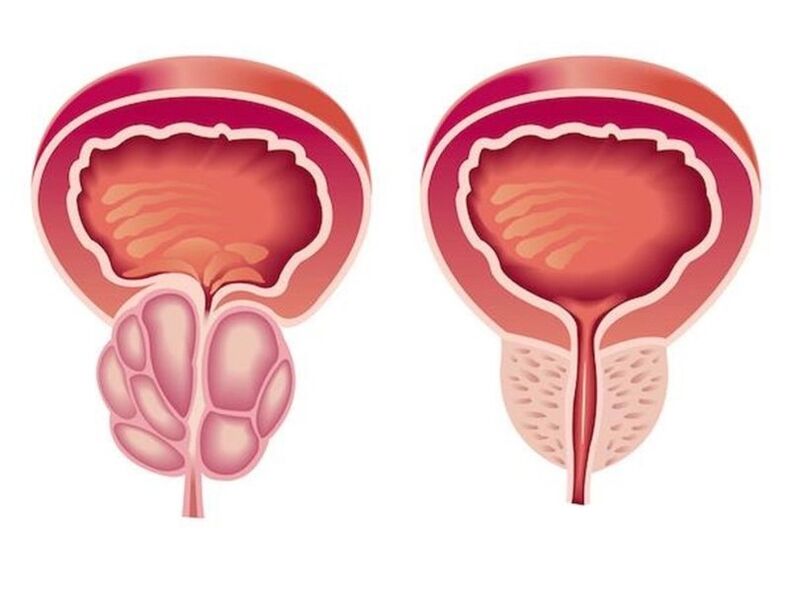
As a result of the inflammation in chronic prostatitis, the volume of the prostate that tightens the urethra increases. The lumen of the ureter decreases. The patient has frequent urination, an incomplete feeling of bladder emptying. As a rule, the unhappy phenomena are expressed in the early stages. Therefore, the compensatory hypertrophy of the muscle layer of the bladder and ureters develops. The symptoms of dysuria during this period are weakening, therefore increased again during the decompexes of adaptive mechanisms.
In the initial stages, violations in power can develop, which have manifested themselves differently in different patients. Patients can complain of frequent night erections, delete orgasm or deterioration of an erection. Accelerated ejaculation is associated with a decrease in the level of excitement threshold of the center, which is responsible for obtaining an orgasm. Pain for ejaculation can cause a refusal of sexual activity. In the future, sexual disorders become more pronounced. In an advanced phase, impotence develops.
The degree of sexual disorder is determined by many factors, including the patient's sexual constitution and the psychological mood. Violations of power and dysuria can be due to both changes in the prostate gland and how easily the patient can inspire anything. If it has chronic prostatitis, the inevitable development of sexual disorders and urination disorders is expected. Above all often psychogenic disorders in power and the problems of going to the bathroom develop in suggestive and alarming patients.
Complications
In the absence of a timely treatment of acute prostatitis, there is a significant risk of developing the abscess of the prostate gland. When the purulent focus is formed, the patient's body temperature rises to 39-40 ° C and can acquire a frenetic character. The heat periods alternate with pronounced chills. Acute pain in the perineum complicates urination and makes defecation impossible.
The growth of Edema Edema leads to a delay in acute urination. In rare cases, the abscess opens spontaneously in the urethra or rectum. When it opens in the urethra, the muddy purulent urine appears with an unpleasant pungent smell, when it opens in the rectum, the feces contains pus and mucus.
For chronic prostatitis, a path similar to waves with periods of prolonged remissions is characteristic, during which inflammation in the prostate proceeds latent or manifests itself in extremely scarce symptoms. Patients, who distinguish nothing, often stop treatment and convert only with the development of complications.
The most frequent complication of the chronic process is the inflammation of the testicles and the appendages of the testicles and the inflammation of the seed bubbles. The result of these diseases often becomes infertility.
Diagnostics
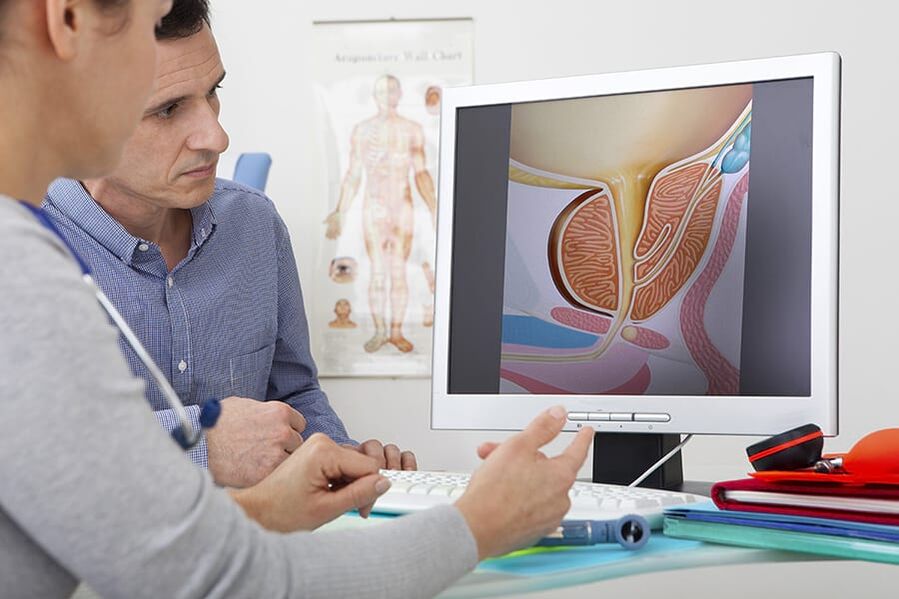
A characteristic clinical picture simplifies the process of diagnosis in acute and chronic prostatitis. It is mandatory:
- Rectal prostate study
- The enclosure of the secretion of the prostate gland to determine the sensitivity of the microflora (sowing the secret of the prostate and sowing urine to bacteria).
- An ultrasound of the prostate is carried out to identify structural changes (tumors, cysts, adenoma) and the differentiation of prostatitis from other diseases
- A spermogram to exclude or confirm the development of infertility.
Treatment of prostatitis
Acute prostatitis treatment
Patients with an acute process without complication undergo a treatment course with an outpatient urologist. With serious intoxication, suspicion of a purulent process, hospitalization is indicated. Antibacterial therapy is performed. The drugs are selected taking into account the sensitivity of an infectious agent. Antibiotics are widely used that can penetrate well in prostate tissue (ciprofloxacin, etc. ).
With the development of a delay of acute urination, against the background of prostatitis, they resort to the installation of a special tube and not to a urethral catheter, because there is the danger of formation of an abscess of the prostate. With the development of the ascess, a transrettal or uandoscopic urethral opening of the abscess is carried out.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
The treatment of chronic prostatitis should be complex, including ethitropic therapy, physiotherapy, correction of immunity:
- Antibiotic therapy. Long-term antibacterial courses are prescribed to the patient (within 4-8 weeks). The selection of the type and dosage of antibacterial drugs, as well as the determination of the duration of the course of treatment is carried out individually. The drug is chosen based on the sensitivity of the microflora based on the results of the sowing of the urine and the secret of the prostate.
- Prostate massage. The gland massage has a complete effect on the organ concerned. During the massage, the inflammatory secret accumulated in the prostate gland is crushed into the ducts, then enters the urethra and removes from the body. The procedure improves blood circulation in the prostate, which allows you to minimize stagnation and provides the best penetration of antibacterial drugs in the tissue of the affected organ.
- Physiotherapy. To improve blood circulation, laser exposure, ultrasound waves and electromagnetic vibrations are used. If it is impossible to perform physiotherapy procedures, the patient prescribed hot medicinal microclisms.
In chronic long -term inflammation, a consultation of an immunologist is indicated for the choice of tactics of immunocorrigative therapy. Recommendations are given to the patient for a change in lifestyle. The introduction of some changes to the lifestyle of a patient with chronic prostatitis is both therapeutic and a preventive measure. The patient is recommended to normalize sleep and wakefulness, to establish a diet and conduct moderate physical activity.

Forecast and prevention
Acute prostatitis is a disease that has a chronic tendency pronounced. Even with adequate timely treatment, more than half of patients, chronic prostatitis becomes result. Recovery is far from always possible, however, with the correct sequential therapy and compliance with the doctor's recommendations, it is possible to eliminate the unpleasant symptoms and obtain a long persistent remission in the chronic process.
Prevention consists in the elimination of risk factors. Hypothermia, alternative sedentary work and with periods of physical activity and eating regularly and completely, must be avoided. With constipation, they should be used laxative. One of the preventive measures is the normalization of sexual life, since both excessive sexual activity and sexual abstinence are risk factors in the development of prostatitis. If the symptoms of a urological disease or sexually transmitted, it is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner.

























